一、方法是什么
在我看来,方法可以看作是和C语言或C++中的函数一样的东西,就是一段可以被重复调用的方法块。Java中的方法可分为内置方法和自定义方法。下面将开始逐一进行介绍。
二、内置方法
我们在刚开始用Java编写程序时,用到最多的便是Math类
Math类提供了很多实用的方法,用来计算常用的数学函数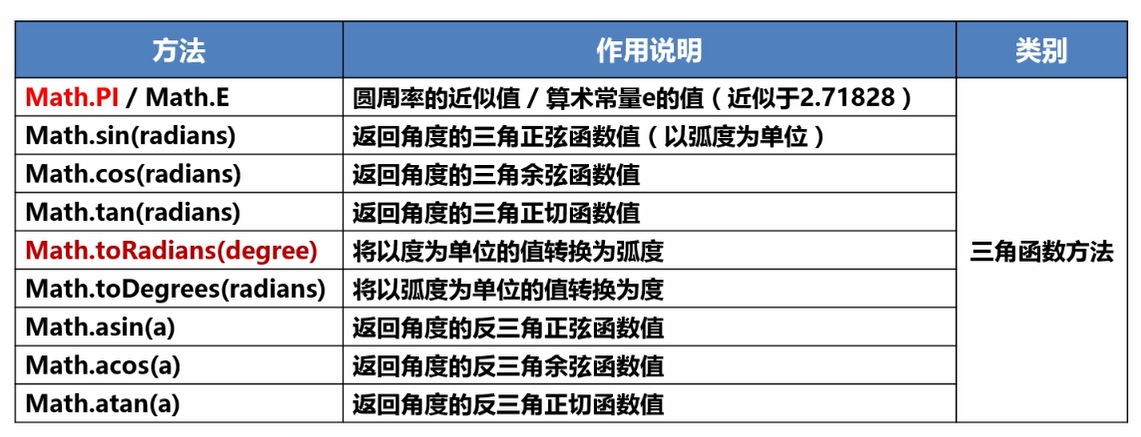
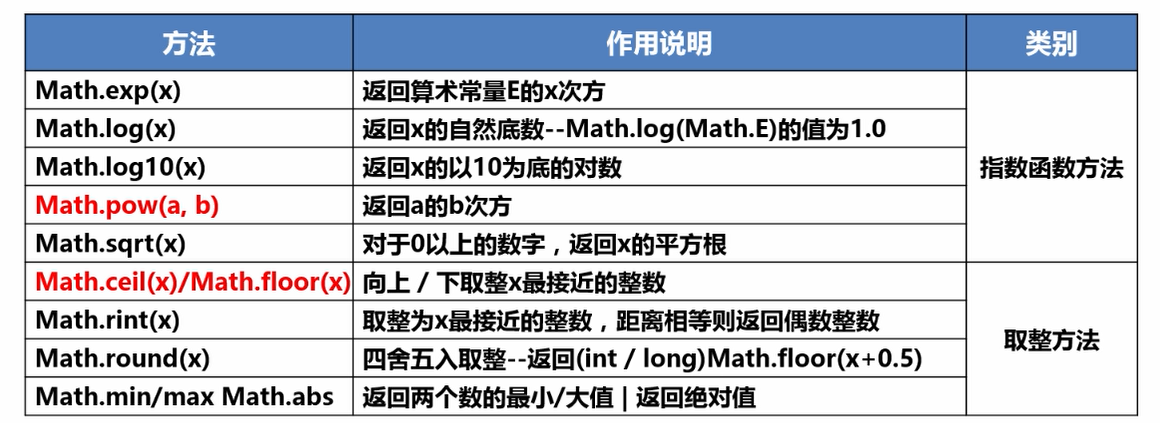
Java中还用很多类似的方法,在调用之前一定要记得导入相应的包,不然程序会报错。

用import导入相应的包即可。
三、自定义方法
限制条件:自定义方法必须在主类中定义,并且由主方法直接调用的方法形式。自定义方法通常通过以下方式进行定义。
1
2
3
4
| public static 返回类型 方法名称([参数类型 变量, ......]) {
方法体代码;
[return [返回值];]
}
|
- 修饰符:方法的修饰符比较多,有对访问权限进行限定的,有静态修饰符static,还有最终修饰符final等,这些修饰符在后面的学习过程中会逐步介绍
- 返回值类型:用于限定方法返回值的数据类型
- 参数类型:用于限定调用方法时传入参数的数据类型
- 参数名:是一个变量,用于接收调用方法时传入的数据
- return关键字:用于结束方法以及返回方法指定类型的值
- 返回值:被return语句返回的值,该值会返回给调用者
看到很多文章都是将自定义方法分为四种:无参无返回值、无参有返回值、有参无返回值和有参有返回值,其实通过上面的通式很容易就能理解以上四个概念,我来主要说一下有参方法的一些细节
1、按值传递的机制
- 按值传递(pass-by-value)
- 为方法传递参数时,参数不会直接传递给方法,而是先制做参数值的副本,存储在栈上,再使这个副本可用于方法,而不是使用初始值。
2、不定长度的参数
通过下面的求平均成绩的代码感受一下,怎样传递不定长度的参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class blogTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] score = {99, 85, 82, 63, 60};
printAvg(score);
}
public static void printAvg(double ...score) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
sum += score[i];
}
System.out.println("平均分:" + sum / score.length) ;
}
}
|
3、方法重载
- 重载
- 方法名称相同,参数列表不同
- 编译器根据方法签名决定调用哪个方法
假设现在要对三组不同数据类型且每组数据包含两个常量(或字符串)进行选出较大的一个的操作,为了方便起见,定义三个方法且方法名都叫Max,这时就用到了重载,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class blogTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(max(15, 51));
System.out.println(max(1.5, 5.1));
System.out.println(max("Hello", "hello"));
}
public static int max(int num1,int num2) {
return num1 > num2 ? num1 : num2;
}
public static double max(double num1,double num2) {
return num1 > num2 ? num1 : num2;
}
public static String max(String str1,String str2) {
if (str1.compareTo(str2) > 0) {
return str1;
}else {
return str2;
}
}
}
/*
运行结果:
51
5.1
hello
*/
|
注意:
1、有时调用方法会有两个或更多可能的匹配,编译器无法判断哪个更为精确,这称为歧义调用(ambiguous invocation)
2、被重载的方法必须具有不同的参数列表,不能基于不同修饰符返回值类型来重载方法
以上这些都是在自定义方法时需要注意的一些细节,最后分享两个自定义方法的例子,能够较快提升对自定义方法的理解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 十六进制和十进制之间的转换
*/
public class HexToDecimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个整形数字:");
int decNum=input.nextInt();
System.out.println(DecToHex(decNum));
System.out.println(HexToHDec(DecToHex(decNum)));
}
/**
* 调用方法将十进制转换为十六进制
* @param decNum 要转换的十进制数字
* @return 转换成十六进制的数字(以字符串的方式返回)
*/
public static String DecToHex(int decNum) {
String hex ="";
while (decNum!=0) {
int temp = decNum%16;
if (temp>=0&&temp<=9) {
hex = temp+hex;
}else if(temp>=10&&temp<=15) {
hex=(char)(temp-10+'A')+hex;
}
decNum/=16;
}
return hex;
}
/**
* 十六进制转换为十进制
* @param hex 要转换的十六进制字符串
* @return 转换成功的十六进制数
*/
public static int HexToHDec(String hex){
int decNum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < hex.length(); i++) {
char tempChar=hex.charAt(i);
if (tempChar>='0'&&tempChar<='9') {
decNum+=(tempChar-'0')*Math.pow(16, hex.length()-i-1);
}else if (tempChar>='A'&&tempChar<='F') {
decNum+=(tempChar-'A'+10)*Math.pow(16, hex.length()-i-1);
}
}
return decNum;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("请输入今天是星期几:");
int dayOfWeek = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
ShowWeekDayByChinese(dayOfWeek-1);
ShowWeekDayByJapanese(dayOfWeek-1);
ShowWeekDayByEnglish(dayOfWeek-1);
}
private static boolean isRight(int dayOfWeek) {
if (dayOfWeek<0||dayOfWeek>6) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 以中文的方式打印星期几
* @param dayOfWeek 1-7之间的整形数字,用来表示星期几
*/
public static void ShowWeekDayByChinese(int dayOfWeek) {
String[] weekday = {"星期一","星期二","星期三" ,"星期四","星期五","星期六","星期日"};
if (isRight(dayOfWeek)) {
System.out.println(weekday[dayOfWeek]);
return;
}
System.out.println("输入有误!请输入1-7之间的数字");
}
/**以日文的方式打印星期几
*
* @param dayOfWeek
*/
public static void ShowWeekDayByJapanese(int dayOfWeek) {
String[] weekday = {"月曜日","火曜日","水曜日" ,"木曜日","金曜日","土曜日","日曜日"};
if (isRight(dayOfWeek)) {
System.out.println(weekday[dayOfWeek]);
return;
}
System.out.println("输入有误!请输入1-7之间的数字");
}
/**以英文的方式打印
*
*/
public static void ShowWeekDayByEnglish(int dayOfWeek) {
String[] weekday = {"Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday" ,"Thursday","Friday","Saturday","Sunday"};
if (isRight(dayOfWeek)) {
System.out.println(weekday[dayOfWeek]);
return;
}
System.out.println("输入有误!请输入1-7之间的数字");
}
}
|
Author:
Allen Xue
License:
Copyright (c) 2019 CC-BY-NC-4.0 LICENSE
Slogan:
To be or not to be,that is a question.


